The Scenario
A student recently approached me to review their dissertation proposal, which had been rejected by their school’s proposal committee. I had not been involved in the proposal. One of the key issues was that the student had confused the concepts of mediation and moderation, which led to flaws in the argument, hypotheses, statistical methods, and potential conclusions.
This is a common challenge for students working with quantitative methods. Many students struggle to distinguish between mediation and moderation, even though these concepts are fundamental to research design and analysis.
The Issue
Mediation and moderation address distinct research questions:
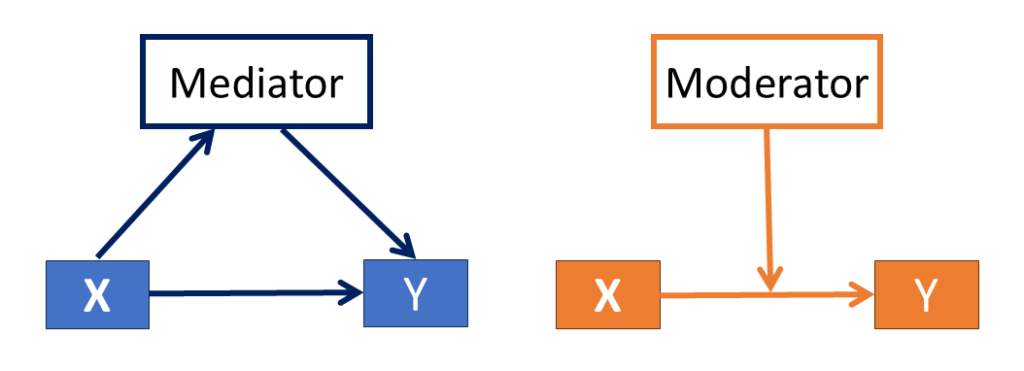
- Mediation focuses on how or why an effect occurs, i.e. the reason for the relationship between the independent variable and the dependent variable. For example, Comprehension could mediate the relationship between the Hours of study (X) and Examination score (Y) as more hours could increase comprehension, which, in turn, could increase the examination score. The mediator is caused by X and, in turn, causes Y. See the figure on the left.
- Moderation focuses on the context of the relationship between the independent and dependent variables. This refers to changes in the relationship depending on when or for whom an effect occurs. For example, the relationship between Hours of study (X) and Examination score (Y) may differ depending on the Age of the student. So, age would be a moderator as it supplies the context of the relationship, and hours of study cannot cause age. See the figure on the right.
The Solution
If in doubt, have a look at whether the independent variable X can feasibly cause the variable you are questioning (M). If it cannot, the variable M cannot be a mediator because the mediator must be the result of the independent variable and the cause of the dependent variable. The variable M may thus be a moderator and you would then examine it as a moderator or interaction term.
On the other hand, if the variable you are questioning (M) could be caused by the independent variable X and, in turn, cause the dependent variable (Y), you would then examine it as a potential mediator to see if the relationship between X and Y is weakened after controlling the effect of M.
The Key Takeaway
Simply put, mediators explain the process, whereas moderators alter the context.
Contact me at [email protected] if you need help with your statistical analysis or any aspect of your dissertation.